With the rapid development of information technology, businesses have constantly improved and applied ICT to switchboard operations. Virtual switchboard technology and the terms VOIP GATEWAY were also born from here.
In the article below, BellSystem24-Vietnam will help you synthesize and systematize all basic information about VOIP GATEWAY, optimize switchboard technology to break through sales in the future.
What is Voip gateway?
Voip Gateway is a specialized device used to convert two-way signals between analog phones, mobile numbers, waves... into IP format, with the aim of creating communication between signals other than the current popular signal, IP.
Operational diagram and components of Voip Gateway system
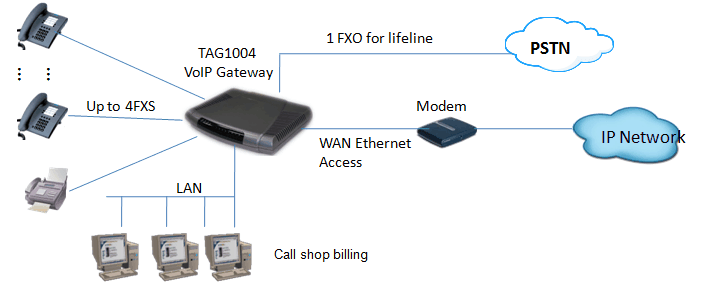
The Voip Gateway system includes 5 basic components as follows:
- Gateway: This is a device that converts digital signals to analog signals (and vice versa).
- PBX server (roughly translated as PBX Server) is similar to a proxy server: SIP clients, which can be soft/hardware phones, register with the PBX server and when they want to make a call, they ask the IP PBX to establish a connection. The PBX server has a directory of all phones/users and their corresponding SIP addresses and is therefore capable of connecting internal calls or routing external calls through a VoIP gateway or VoIP service provider.
- VoIP server (tentatively translated as central servers) have the function of routing and securing VoIP calls. The name of this central server varies depending on the network, specifically: H.323 network is gatekeeper; SIP network is SIP server.
- Terminal (End user equipments): Can use hardware devices or Softphones installed on personal computers such as: Skype, Cisco IP Communication, Ekiga, Microsoft Netmeeting, SIPSet, GnomeMeeting, ... Hardware uses phones with pure IP Phones specializing in VoIP.
- IP phone: are phones specifically designed for VoIP. IP phones do not need a VoIP Adapter because they have a built-in VoIP adapter that can connect directly to VoIP servers.

Functions of Voip Gateway
Voip Gateway is used in 2 basic cases:
-
Convert PSTN Phone Calls/Lines to Voip/SIP
This is the most important function of Voip. When you use Voip Gateway device to convert signals from suppliers Viettel, Vinaphone, Mobifone, FPT... and sources from CO, trunk E1/T1/J1, Bri, SS7... connecting to the internal data network system of the enterprise
-
Connect a traditional PBX/telephone system to an IP network
Voip Gateway converts signals from traditional analog switchboards to IP connections, helping businesses contact more customers through Softphone software, iPhones, etc.
In this case, Voip Gateway helps the unit save significantly on line costs, only needing to connect multiple branches of the Internet switchboard, LAN/WAN internal network
Types of Voip gateway devices
There are two basic types:
-
Type of Voip gateway device mounted on the host computer
This is a type of device mounted in a PCI, ePCI slot. In which:
– 1 Connector to service provider
– 1 Head connects directly to Softswitch IP-PBX switchboard
Some Asterisk cards for this type of Voip Gateway device mounted in the server: OpenVox Card, Sangoma Card, Digium Card
-
Type of Voip gateway device outside the computer
There are 2 types of devices as follows:
+ FXO standard Voip Gateway type: This is a device with 2 ends, 1 end connects to the telecommunications service provider and one end connects to the Lan/Wan network port with RJ45 ports.
+ Standard FXS Voip Gateway: This is a device that allows you to utilize old analog phones. You just need to connect these phones to the RJ11 port of the Voip Gateway device.
Why should businesses use Voip Gateway?
VoIP was born to exploit the efficiency of data transmission networks, exploit the flexibility in developing new applications of the IP protocol and it is applied on a global network, the Internet. Technological advances have brought VoIP the following advantages:
-
Reduce call costs
The main advantage of IP telephony over current telephone services is the ability to provide low-cost long-distance calls with acceptable quality. If IP telephony services are deployed, the cost of a long-distance call will be equivalent to the cost of Internet access. The reason for such low costs is that voice signals transmitted over IP networks have the ability to use channels very efficiently. At the same time, advanced voice compression techniques that reduce bit rates from 64Kbps to as low as 8Kbps combined with the fast processing speed of today's microprocessors allow real-time voice transmission to be possible with much lower bandwidth resources than with older techniques.
-
Scalability
While switchboard systems are often closed systems, it is difficult to add new features, while devices in the Internet often have the ability to add new features. This flexibility gives IP telephony services the ability to expand more easily than traditional telephony.
-
No control information is required to establish a physical channel.
The packet of information in an IP network is transmitted to its destination without any channel setup. The packet only needs to carry the address of the final recipient for the information to reach its destination. Therefore, the call control in an IP network only needs to focus on the call function without having to focus on the channel setup function.
-
Bandwidth Management
In circuit-switched telephony, the bandwidth resources provided for a call are fixed (a 64Kbps channel), but in IP telephony, the allocation of resources for calls is much more flexible. When a call is in progress, if the network traffic is low, the bandwidth allocated for the call will provide the best possible voice quality, but when the network traffic is high, the network will limit the bandwidth of each call to a level that maintains acceptable voice quality in order to serve the most people at the same time. This is also a factor that increases the efficiency of IP telephony. Such economical bandwidth management allows people to think about more advanced services such as conference calling, which is not possible with old circuit-switched technology because of its high cost.
-
Multiple service features
The flexibility of IP networks allows for the creation of many new features in voice services such as: Providing information about the caller or an IP phone subscriber can have many contact numbers with only a single terminal.
-
Multimedia capabilities
During a call, users can talk and use other services such as file transfer, data sharing, or viewing images of the other person.
-
Use effectively
As we know, VoIP transmits voice over the Internet and uses the IP protocol. Today, IP is the most widely used network protocol and there are many applications being exploited based on IP network protocols. VoIP can combine these applications to improve network efficiency. VoIP technology is mainly used in combination with computer networks, so it can take advantage of the development of information technology to improve efficiency. Software will greatly support the exploitation of VoIP network services. The more information technology develops, the more effective the exploitation will be, and many new services will appear to support users in all fields.







