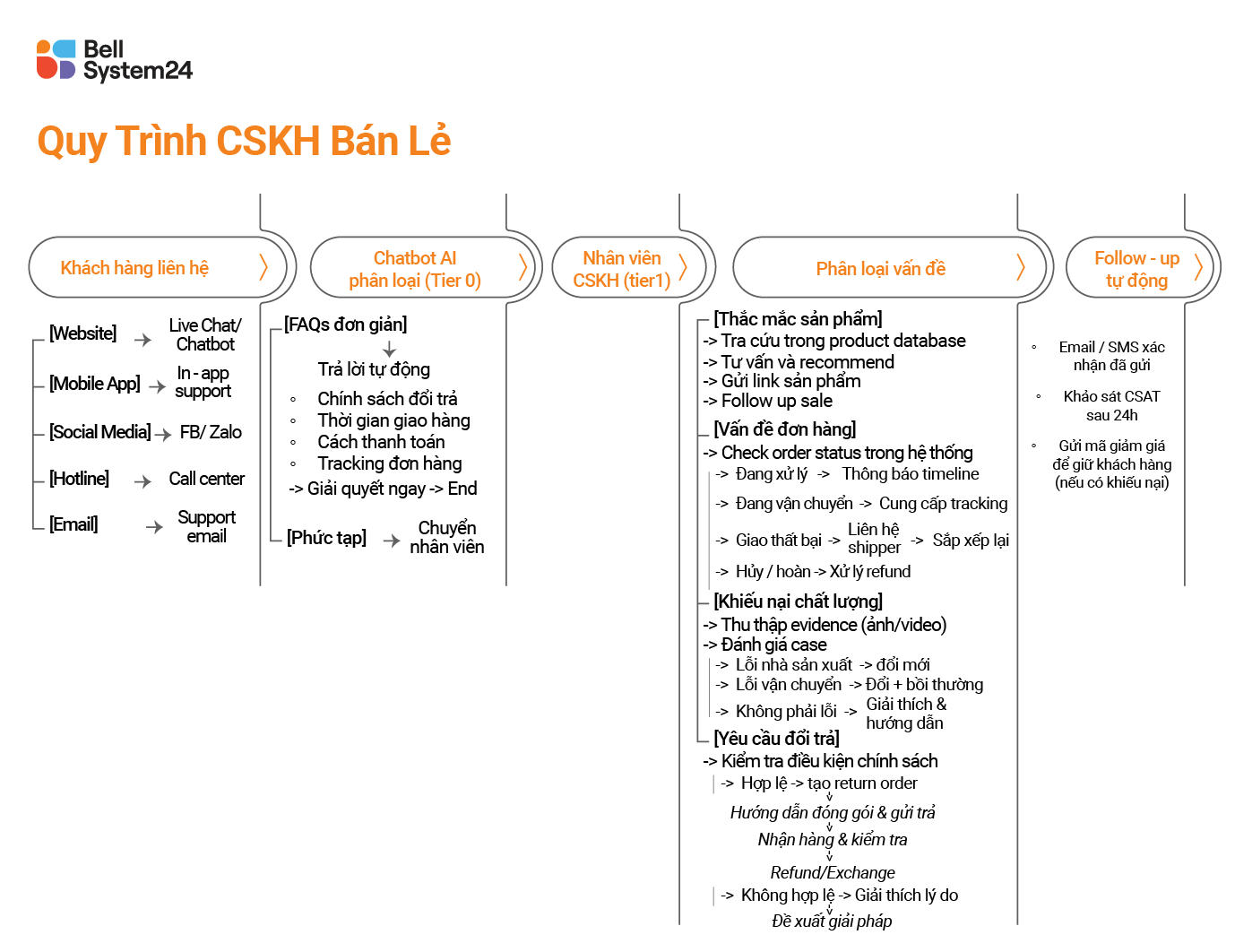
What is Call Center?
A call center is a business's call center, capable of receiving, processing, and handling multiple calls simultaneously, often used to perform activities. customer serviceSales. It can be considered an important channel of communication between customers and businesses.

Call Center Application.
With superior call support features, call centers are often used to.
- Customer care, Customer surveys, consulting, and information provision.
- Telesales. telemarketing, schedule an appointment.
Why is Call center popular?
Before call centers came into existence, businesses had to manually receive and handle customer calls. But imagine receiving thousands of calls every day. At this point, a system is needed to handle the enormous workload, and that is why Call Centers emerged with a range of superior calling features.
Call Center Features.
| Features | Function | Detail |
|---|---|---|
| IVR | Automatic voice interaction via telephone, by playing a pre-recorded audio clip | Link |
| ACD | Distribute calls to the appropriate employees | Link |
| Skill-based routing | Call routing based on operator skills | Link |
| Customer Management | Store and manage customer information, sales data, and interaction history using CRM | Link |
| Auto call | Automatically dial a list of numbers without manually dialing each number. | Link |
| Report | Report on ticket status, agent performance, and predefined metrics in the system | Updating |
| Monitoring | Monitor calls in real time. Allow listening in or intervening in ongoing calls. | Updating |
| Speech analysis | Analyzing call information based on voice | Link |
Build a Call Center.
To build a complete Call Center, the following steps are required.
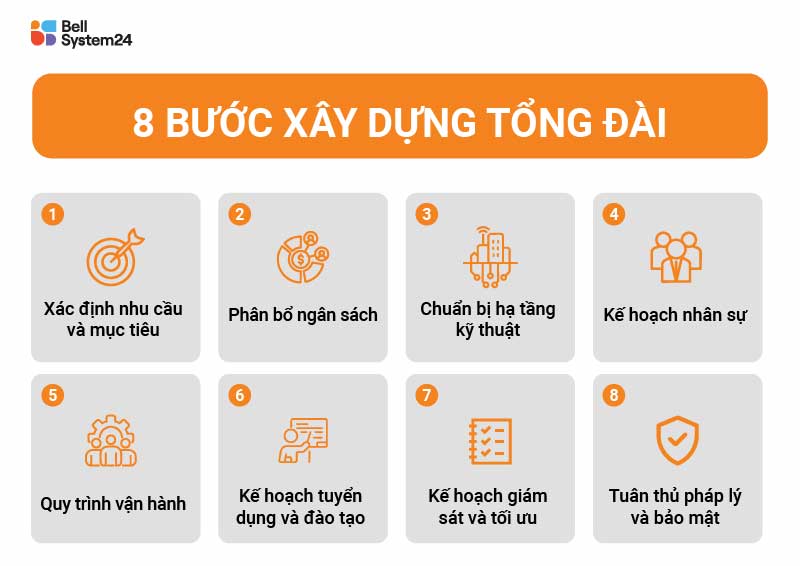
1. Identify needs and objectives
Identify specific needs and objectives: Customer service, sales, cost optimization, etc.
Call center type:
- Inbound: Receiving customer calls
- Outbound: Outgoing calls
- Hybrid: combining both
Scale: Calculate the number of employees and infrastructure needed to handle the interaction volume.
2. Budget allocation
Determine the costs of building and maintaining the switchboard, including:
- Infrastructure: Rent office space, desks, chairs, etc.
- Hardware: Computers, phones, headphones, servers, and other connected devices.
- Software: Software development or licensing fees (typically including: Call center software, CRM, other supporting software)
- Staff: Salary, insurance, other benefits, etc.
- Operating costs: Electricity, water, internet, phone bills, maintenance fees.
3. Prepare technical infrastructure
- Infrastructure: Location, tables, chairs, etc.
- Hardware: Computers, phones, headphones, servers, and other connected devices.
- Software: Software development or licensing fees (typically including: Call center software, CRM, other supporting software)
4. Human Resources Plan
Depending on the call center's objectives, the structure and scale of personnel vary. Many call centers estimate the number of personnel based on (1) call volume, (2) Average call handling time.
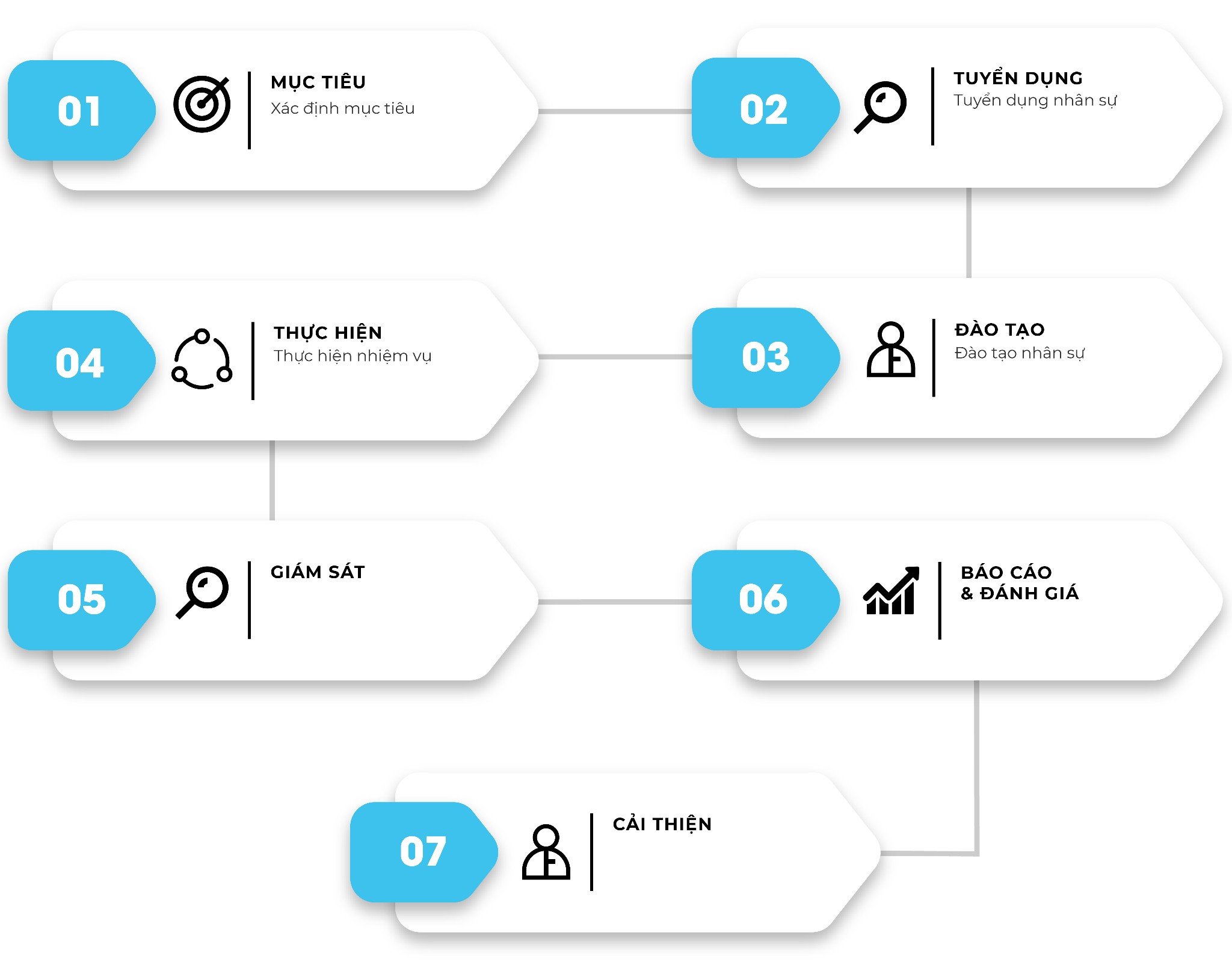
5. Operating procedures
- Develop a call handling process
- Processes, evaluation standards, and performance reports.
- Call script: Standardize the content of exchanges.
- Contingency plans in case of an incident: Reconnect, resolve customer complaints.
6. Recruitment and Training Plan
Based on the objectives and call center operations, develop a recruitment and training plan.
Recruitment
- Determine the number and roles of employees and plan recruitment.
- Develop job descriptions and recruitment criteria.
Train
- Training program on knowledge, professional skills, and entry-level skills.
- Monitoring and post-training evaluation.
- Retraining and advanced training during employment.
7. Call center monitoring and optimization plan
Businesses can measure Call Center performance through KPIs proposed. The evaluation criteria will differ between the Customer Care Center and Sales.
Call centers implemented through outsourcing will measure their operational effectiveness based on:
- Cost per call
- Revenue & Profit Achieved
- Number of completed calls
- Customer waiting time
- Missed call
- Time for discussion, etc.
8. Legal compliance and security
Develop legal compliance and data security regulations for the government and relevant parties.
Some effective solutions:
- Develop work processes and information security in accordance with ISO 27001 standards.
- Secure user information using tools (mask phone numbers, emails, etc.).
- Access permissions based on device or employee level.
- Obtain the customer's 'consent' to make advertising calls (in accordance with Decree 91/2020/NĐ-CP of the government).
Call Center Operation Process.
See also: Call center metrics and evaluations
Forms of call center deployment
There are three common types: in-house call centers, outsourced call centers, and offshore call centers.
| Form | In-house call center | Domestic Call Center Rental (Onshore) | Outsource call center services |
|---|---|---|---|
| Description | The form in which the enterprise builds and operates its own call center | Outsourcing a specialized unit to build and operate the call center. | The practice of hiring a unit located in another country, typically one with low labor costs and political stability. |
| Advantages | - High level of autonomy, flexibility in customizing systems and operational processes. - Understand the product, customers, and corporate culture. | - Rapid deployment, saving time and resources. - Negotiate the target and the lessee must comply. - Flexibly adjust the scale according to each time period. | Cost savings |
| Disadvantages | - High initial setup costs. - Difficult to operate if the business lacks experience, as this is a specialized field. - Requires significant time and resources to operate. | - Difficulties in managing and coordinating with suppliers. - Risks related to safety and information security. - In addition, BPO providers also vary in capability, so businesses need to carefully evaluate them when making their selection. | - Language and cultural limitations - Difficulties in coordination and control. |
| Suitable for | The company has sufficient financial capacity and experienced personnel to operate a call center. The call center is considered an indispensable part (core team) throughout the entire operation. | Businesses want to outsource to increase flexibility or need to deploy call centers at certain times. Businesses want to reduce their workload and focus on core business activities. | Multinational companies want to reduce call center costs. |
Summary of metrics to measure call center performance

Average Handling Time (AHT)
Average Handling Time (AHT) is the average amount of time a call center agent needs to complete an interaction with a customer.
Calculation formula: AHT = Waiting time + Talking time + Data processing time
First Contact Resolution (FCR) rate
First Contact Resolution (FCR) is an important Call Center metric that measures the ability to thoroughly handle and resolve customer requests or issues during the first contact without the need for follow-up or recontact. This metric directly reflects the operational efficiency of the Call Center and the level of customer satisfaction.
Service Level (SL)
Service Level (SL) is one of the most important metrics in the set of criteria for evaluating call center operational quality. It should also be noted that achieving a service level of 100% will never happen due to the impact of issues related to the Call Center system, external factors, and the need to have a very large team of call center agents.
Net Promoter Score (NPS)
Customer loyalty score, or NPS (Net Promoter Score), is one of the most popular call center metrics for measuring customer satisfaction and loyalty to a company's services or products. The standard customer loyalty score (NPS – Net Promoter Score) is 8 (on a scale of -0 to 10). NPS also varies greatly depending on the industry. But in general, the higher the score, the better.
NPS calculation formula: NPS = % Promoters – % Detractors
Maximum operating efficiency (MO)
Maximum Occupancy (MO) is a call center metric that measures an agent's actual work capacity based on the maximum productivity (100%) they can achieve. The average MO in the call center industry is 83.3%.
See more details on how to calculate call center metrics HERE
Call Center of the future.
Omni-channel trend
The rapid development of technology has led to increasingly diverse and flexible customer contact channels. As a result, businesses want their contact centers to be able to respond to many different channels. At this time, Contact Center born with the ability integrated multi-channel response: Voice calls, chat, Email, Social media, Website,.. Contact Center is rapidly developing and gradually becoming more and more popular because of its superior benefits.
Automation
Customers want faster service. Customer service centers use artificial intelligence (AI) to automate simple tasks, reducing customer wait times. This allows for a reduction in the number of call center agents, who can then focus on handling complex cases. According to Gartner, by 2025, 75% of customer service centers will integrate AI.

However At the present time and in the near future, Call Centers will remain the most widely used call center platform, as telesales, telemarketing, and customer service via voice channels are still effective.