What is CRM?
Customer relationship management, or CRM, is a strategy that helps businesses manage customer information in a systematic and effective manner.
CRM leverages customer information and insights to enhance interaction, sales, and customer care, thereby increasing customer satisfaction and loyalty to the business.
A CRM strategy includes people, processes, and CRM software.
The components of a CRM strategy
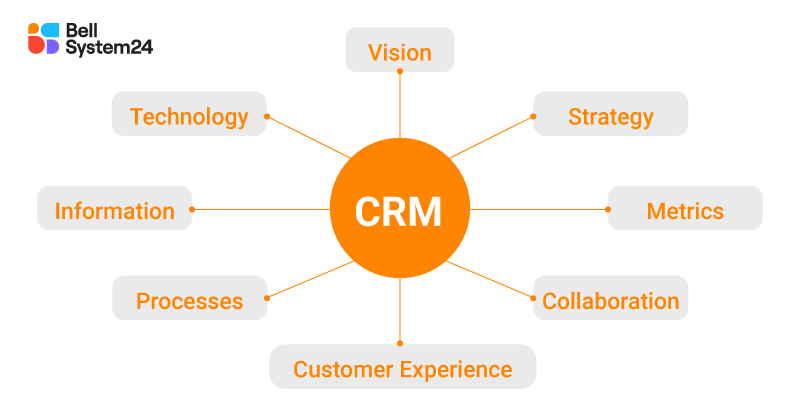
- Vision: Long-term direction for the CRM strategy, describing the ultimate goal related to customers.
- Strategy: A specific action plan to achieve the vision.
- Metrics (Evaluation indicators): Metrics for measuring and evaluating the effectiveness of CRM strategies.
- Collaboration: Coordination between departments and teams within the company.
- Customer Experience: Optimize every touchpoint between customers and businesses.
- Process: Specific steps and activities for implementing CRM.
- Information: Customer data and analytical information.
- Technology: Tools to support the implementation and optimization of CRM strategies.
CRM software
CRM software is a tool for storing and managing customer information, sales data, interaction history, etc., helping businesses manage all information on one platform.

The role of CRM for businesses today
Enhance customer experience
- Understand customers to engage in contextually appropriate interactions.
- Create a seamless customer experience across multiple channels.
- Personalize the message.
- Standardize the process customer service and employee compliance with SLAs.
Improve sales effectiveness
- Analyze customer information to develop appropriate sales methods.
- Help set up automated sales processes.
- Leverage reporting data to develop sales strategies.
Optimize business processes and performance
- Manage information consistently across departments to facilitate seamless coordination.
- Automate processes between departments.
- Work flexibly anywhere.
- Transparent management, standardized according to SLA metrics.
- Cut costs.
Features of CRM software
1. Customer Information Management
As the most important feature of CRM, it is used to store customer information throughout the sales and post-sales process.
1.1 Upload, store, and update customer information
Businesses can upload lists of potential customers, categorize customers, track nurturing progress, perform customer care, and continuously update information.
1.2 Managing contact information (phone numbers, email addresses, etc.)
CRM manages customer contact information, and it can also integrate with Contact center to interact directly with customers and update data directly on the software.

1.3 Customer Journey Management
Store and update information based on interaction history, helping businesses understand which channels customers have used and with whom they have interacted throughout the purchasing cycle.
1.4 Create tickets and support customers
Each customer request is considered a ticket. The CRM system will automatically create and assign tickets to the corresponding departments/employees for processing according to the pre-established SLA. Notify administrators of overdue tickets.
Transaction management and sales process
2.1 Transaction Management
- Record and display complete information about customer transactions, billing information, and inventory withdrawals.
- Automate quotes and contracts.
2.2 Monitoring the sales process
- Store data to track the entire sales process, from the prospect stage, purchase, shipping, post-sales customer care, and warranty.
- Notify the next steps to be taken in the sales process.
3. Marketing features
3.1 Marketing Automation
Integrate marketing tools to automatically send notifications to customers based on specific conditions, for example: Send emails, auto calls, automated chat.
3.2 Customer nurturing
- Segment customers to implement targeted marketing activities.
- Develop scripts and send marketing messages based on specific conditions and contexts. For example: Congratulate customers on their birthdays, wish them a happy new year, etc.
- Create customer files according to the marketing funnel to plan nurturing.
3.3 Marketing Report
Provide detailed reports on marketing effectiveness, which can be integrated with digital marketing tools (such as Facebook, Google ads) to serve as a data feed.
4. Process automation
Help businesses reduce administrative workload and focus on business activities. With CRM, businesses can:
- Establish workflows between departments and individuals, and assign tasks in sequence.
- Monitor work progress, projects
5. Reporting and analysis
CRM data is easily extracted into reports, helping businesses grasp their business situation and make data-driven decisions. Many useful report types include:
- Report on revenue and quantity of goods sold.
- Customer contact volume, customer care index, number of tickets processed.
- Effectiveness of marketing and sales campaigns.
- Analyze purchasing trends and customer preferences.
- Custom reports.
6. Integration with other software
- Integrate with other management software such as CMS, ERP, accounting, etc. to synchronize and avoid data duplication.
- Integrate with communication channels such as Contact centere-commerce platform, webchat to synchronize customer interaction data, creating a seamless customer experience.
CRM Platform Classification
There are three common types of CRM platforms on the market: Cloud CRM, On-premises CRM, and Hybrid CRM.
COMPARISON TABLE
| Criteria | Cloud Customer Relationship Management | On-premises Customer Relationship Management | Hybrid Customer Relationship Management |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | It is CRM software that operates and stores data on a cloud platform. It is often provided as SaaS by companies specializing in CRM. | This is CRM software that is built and stores data on the enterprise's server. The enterprise will build, invest in technology infrastructure, and operate according to its own standards. | It is a combination of Cloud and On-premises CRM. Hybrid CRM will store important data and build CRM processes on a local server. The remaining data and communication channels are stored in the cloud. |
| Advantages | - Low implementation costs - No need to invest in infrastructure - Accessible with internet connection and usable on mobile devices. - Easily scale up or down according to usage needs. | - High customization and adaptability, closely aligned with business processes. - Security mechanisms can be designed according to specific standards. (Highly dependent on the technological capabilities of personnel) | - Leverage the strengths of both Cloud and on-premises platforms. - Supports remote work and mobile devices. - High customizability - High security capability |
| Disadvantages | - Customization capabilities are limited if business processes are overly complex. - Security restrictions may be imposed by the provider. | - High investment costs, complex construction - Technical personnel are required for operation, maintenance, and upgrades. | - High implementation costs - Complex deployment and management |
| Suitable for | Businesses need a CRM with comprehensive features and high flexibility, but do not require overly strict security standards. | Businesses require CRM systems that are tailored to their processes, allowing them to maintain control and ensure data security. Government agencies, banks, hospitals, and multinational corporations often choose this solution. | Businesses with high security requirements but still need flexibility. Companies operating in complex legal environments (e.g., multinational companies). |
Should you use open-source, packaged, or customized CRM?
To find out which type of CRM is right for your business, check out the detailed comparison table below.
COMPARISON TABLE
| Criteria | Open-source CRM | Packaged CRM | Custom CRM |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | CRM has open source code, allowing users to download and modify it as needed. | Solutions are available from providers, featuring standard functionality, easy deployment, and professional support. | Developed from scratch or extensively modified to meet the specific requirements of the business |
| Cost | Free | Flexible by package | High |
| Features | Basically, many plugins are available because there is a large community supporting them. | Comprehensive, suitable for most businesses. Depends on the service provider. | Designed to closely align with the specific needs of the business |
| Security | Self-management and security setup | Performed by the provider | Self-management and security setup |
| Flexible | Highly flexible, depending on customization capabilities | Low flexibility, dependent on the features available from the provider | Highly flexible, depending on customization capabilities |
| Scalability | High. Can be extended via plugins. | High. Expand by upgrading the package. | High. Expand through self-development. |
| Implementation time | A few months, or sooner depending on the IT team | Quickly, a few weeks | A few months, or sooner depending on the IT team |
| Technical requirements | High. A professional IT team is required. | Low. Due to support from the supplier. | High. Requires a professional IT team or dedicated developers. |
| Featured supplier | SuiteCRM, Vtiger, Odoo CRM | Salesforce, HubSpot | Software design and development companies |
| Suitable for | Small businesses, limited budgets | Most businesses. Have customization needs and security requirements that are not too high. | Large enterprises, specialized industries. High customization and security requirements. |
CRM Implementation Process
To successfully implement CRM, there must be commitment from the leadership and members of the company, and members need to clearly understand the role and benefits that CRM brings. Below is the standard CRM implementation process for businesses.
1. Set clear goals
Specify CRM usage requirements: Identify issues to be addressed, such as improving customer service efficiency, enhancing sales processes, and improving interdepartmental coordination.
CRM objectives must align with business objectives and adhere to the SMART principle.
2. Resource allocation plan
The key resources that need to be clearly identified when implementing a CRM system include:
2.1 Human Resources
- Which departments and divisions will use CRM?
- The development of the CRM will be handled by company employees or outsourced. The business needs to clearly identify which departments and personnel will participate in the process of building, testing, and evaluating the CRM in order to plan for a reasonable allocation.
2.2 Investment budget
- Determine the costs of implementing, maintaining, and servicing the CRM.
2.3 Time
- Determine the specific timeframe for implementing CRM.
3. Select the appropriate CRM solution
Based on actual needs and budget, businesses can choose the appropriate CRM solution, keeping the following points in mind:
- Assess the flexibility and scalability of the CRM in the future.
- Ability to integrate with other software in the future.
- Reputable service provider, professional support.
4. Standardize and clean the data
Data is like the knowledge base of CRM. Before implementing CRM, businesses need to do the following:
- Clean and standardize existing data to prepare it for import into the system.
- Develop a standard data entry procedure to ensure that the data entry process is always followed accurately and consistently.
- Develop security measures, data classification, and encryption if necessary.
5. Training the workforce
- Communication plan: Ensure that all employees in the company understand the role and use of CRM in their work. The company can organize regular communication programs about CRM.
- Develop a direct training plan for personnel using CRM, which may combine online and offline training.
- Develop a guidance channel and a set of user guides.
6. Testing
After completing the above steps, it's time to test the CRM. Simulate business scenarios to test it.
- Test all features by conducting trials on multiple devices and with different users.
- Identify security vulnerabilities and system errors that may occur in many cases.
7. Implementation and continuous improvement
After undergoing a testing phase, the company can implement the CRM system. The company can test it in phases or in a few small departments before implementing it fully.
- Always monitor performance to address issues in case of errors.
- Monitor performance and compare it with the KPIs set at the beginning.
- Collect user feedback and suggestions regarding difficulties or features that need to be added during use.
- Perform data backups and conduct regular maintenance checks.
Inc
Vietnam's No. 1 Contact Center & BPO Provider
Experience in implementing customized CRM for hundreds of businesses since 2006.









