According to research by Zendesk, 61% customers are willing to switch to a competitor after just one bad service experience. Furthermore, 95% dissatisfied customers will share their negative experiences with others.
One customer service process được chuẩn hóa không chỉ phòng tránh khủng hoảng, mà còn là điểm khác biệt giúp doanh nghiệp duy trì khách hàng trung thành trong kỷ nguyên cạnh tranh khốc liệt.
A professional customer service process delivers three core benefits
- ConsistencyAll customers receive service experience equivalent, regardless of which employee they interact with, which channel they use, or when they interact.
- ScalabilityAs your business grows, you can quickly hire new employees without worrying about a decline in service quality.
- Measurable: Easily measure KPIs, identify bottlenecks, and continuously improve.
This article will provide a detailed analysis of the components of a process, the Customer Service Process Template Practical and step-by-step guide to building your own customer service process from A to Z.
Core Elements of a Professional Customer Service Process
1. Customer Contact Point
These are all the channels through which customers can interact with the business: hotline, email, live chat, social media, mobile app, and physical store. A professional process must clearly define each touchpoint and how to handle each one.
2. Classification and Prioritization
Not all requests have the same priority. The process needs to have a classification system based on:
- Urgency: Emergency, High, Medium, Low
- Type of problemComplaints, product inquiries, technical support requests, and suggestions.
- Customer valueVIP, loyal customers, new customers, potential customers
3. Scenario Handling
For each situation, a standard scenario is required, including:
- How to greet and acknowledge the issue
- Questions to gather information
- Solution or course of action
- How to conclude and follow up
Customer Care Script not for employees to read mechanically, but rather a framework to ensure that no important steps are overlooked.
4. Authority and Responsibility Assignment
When planning work allocation and building a personnel structure, businesses need to clearly determine:
- Responsibility: Who handles which type of request
- Authority: Level 1 employees can decide for themselves to what extent and when to escalate requests to higher levels.
- Service levelMaximum response time for each customer support case.
5. Tools and Support Systems
Modern work processes must be linked to specific tools such as:
- CRM to store customer information
- Helpdesk for managing tickets
- Knowledge base for quick lookup
6. Measurement and KPIs
Professional processes always come with measurable metrics. See details: 10 Customer Experience Metrics
7. Continuous Improvement Mechanism
The process is not a fixed design; it requires options so that the business has the opportunity to review, analyze, and make improvements. For example:
- Regular review meetings (weekly/monthly)
- Collect feedback from customers and employees
- Analyze data to identify bottlenecks.
- Conduct pilot tests of improvements before widespread implementation
Professional Customer Service Process Templates
Here are 5 Customer Service Process Template Designed for various industries. Each template includes a logic flowchart and practical notes.
Basic Customer Service Process

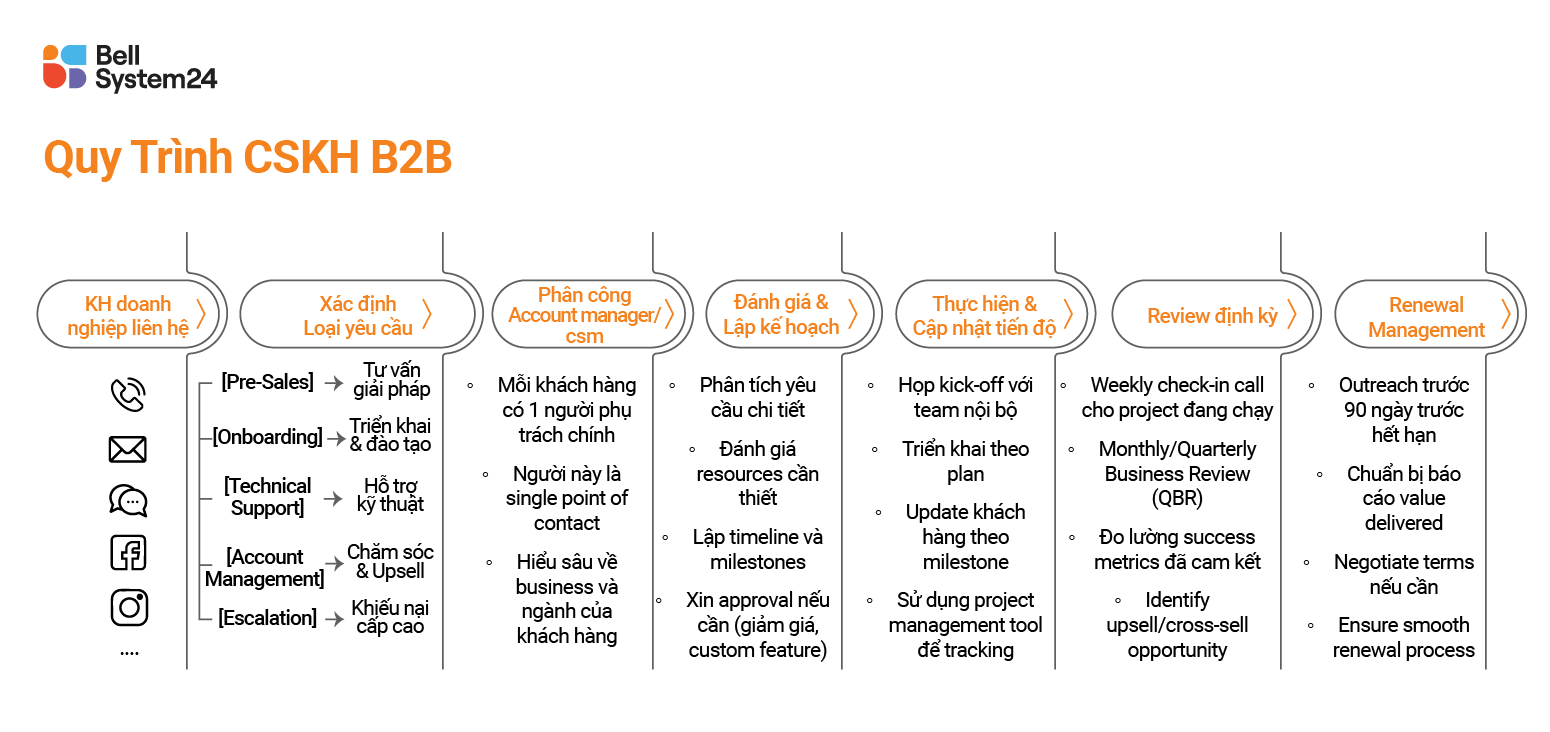
B2B Customer Service Process
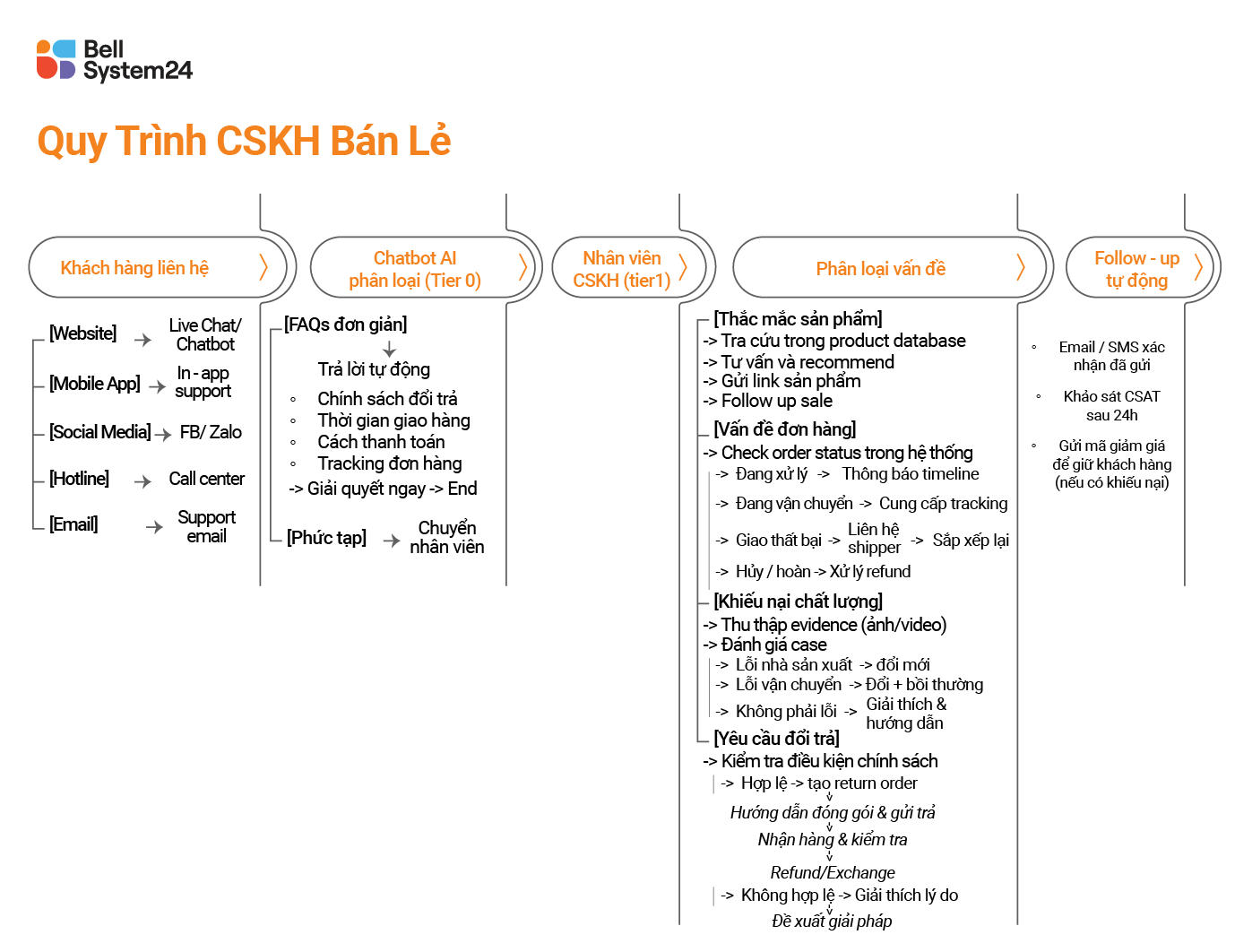
Retail Customer Service Process
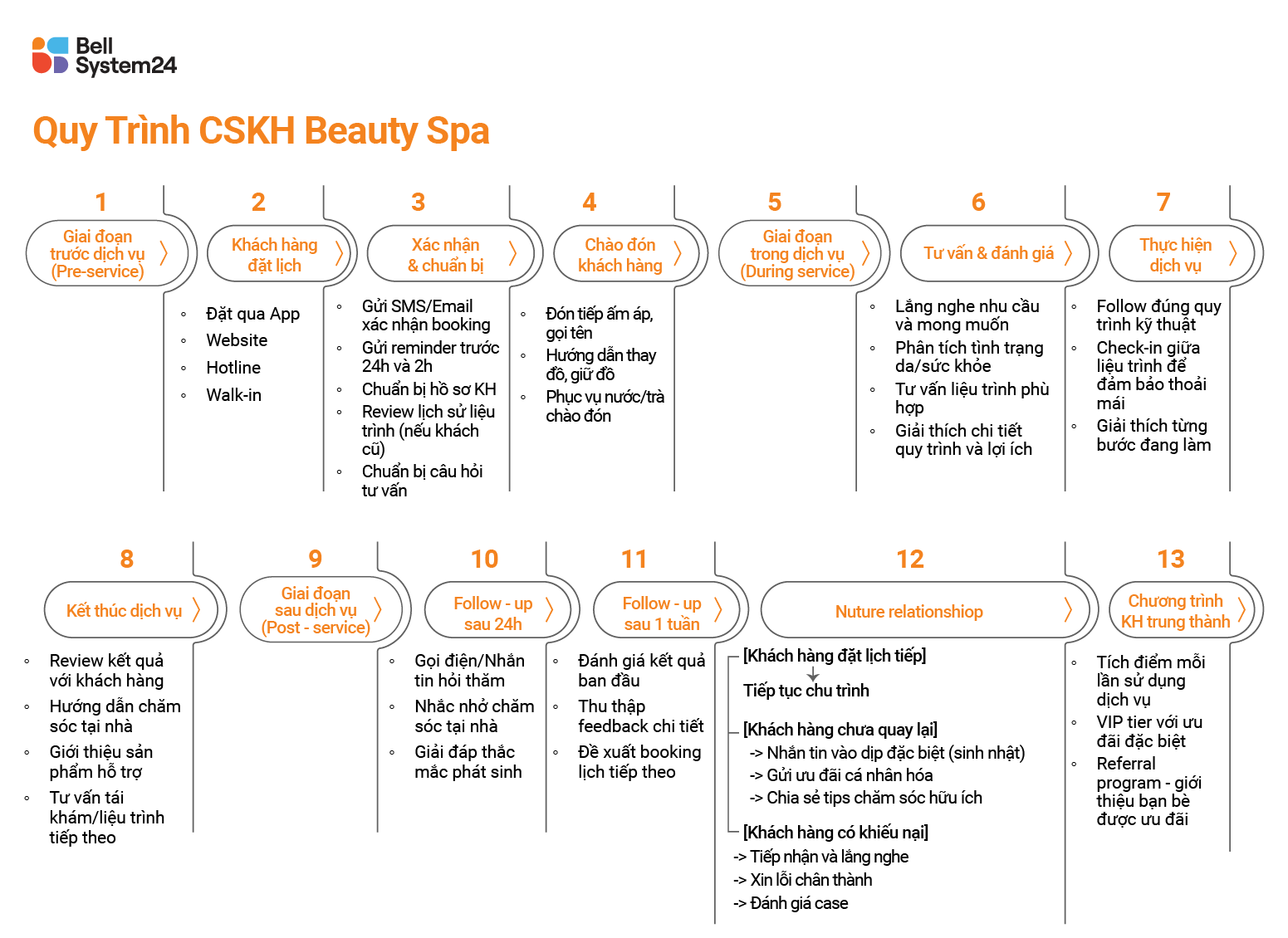
Beauty Spa Customer Service Process
Customer Service Process for Education

6 Steps to Build a Customer Service Process
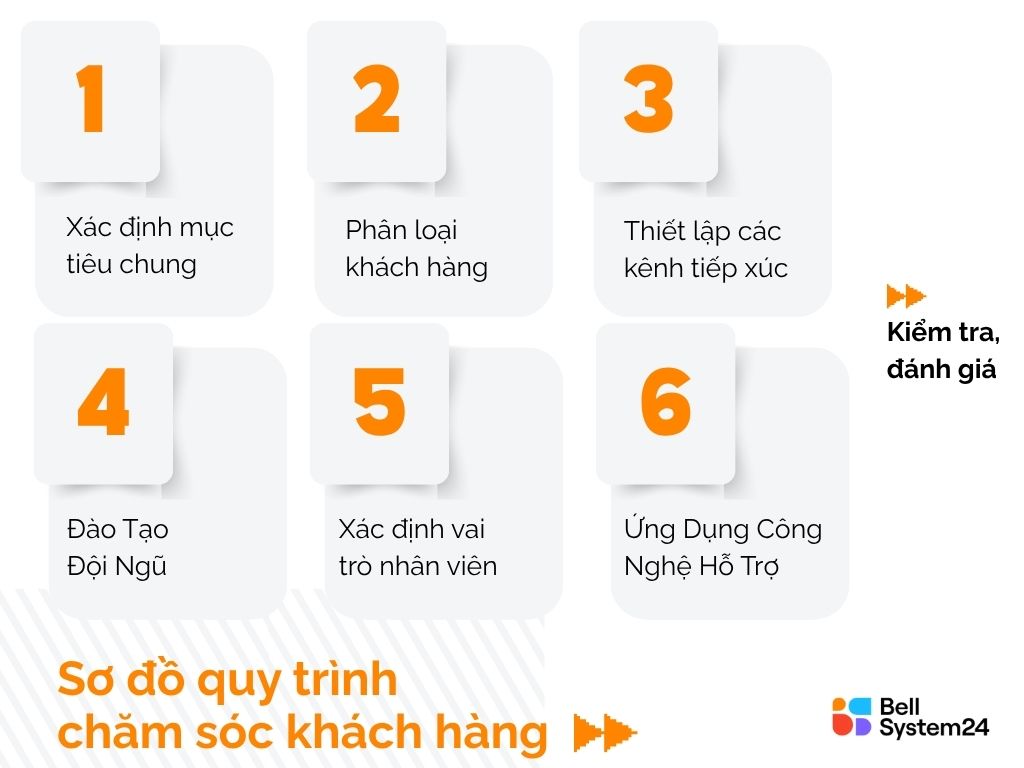
See detailed content: 6 steps to build a customer service process →