Call Center is the switchboard center of the business. It is responsible for receiving customer calls or making outgoing calls.
Call Center plays an increasingly important role as a communication channel that helps businesses implement sales activities, care for and maintain customer loyalty. So what does the setup and operation process of a call center include?

Build a call center deployment plan
1. Define goals and make a plan
The plan will be closely aligned with the actual needs of the business, the more detailed the plan is, the less mistakes will be made in its implementation. Below is some important information to help you plan effectively:
- Determine the situation: What problems does the business need to solve? What are the upcoming business goals?
- Demand: What problems will call center help businesses solve?
- Deployment form: What form will the call center be deployed in? (customer care, telesales, telemarketing). What time frame will the call center operate? On what channels?
- Target: What are the specific goals to achieve (SMART Goals)?
The above ideas are the basis for determining the operation method, staff size and other requirements needed for call center deployment.
2. Building human resource structure and scale
Based on the goals and current situation of the business to calculate the number of employees and organizational chart of the call center department.

Calculate the number of employees
There is no exact formula for calculating the number of call center staff, it will depend on many factors such as:
- Customer interaction traffic (Call volume, chat volume,...)
- Product, service and customer characteristics. This factor depends on each business. The higher the requirements, the longer the interactions will usually take. This factor is calculated by the index AHT and FCR
- Desired service level (SL – Service level): Is the business's expectation of call center quality.
- Fluctuations and contingencies: In addition, businesses also need to calculate the adaptability of the switchboard, especially during peak hours or peak periods (For example: Year-end demand increases sharply).
Build an organizational chart
Sample diagram
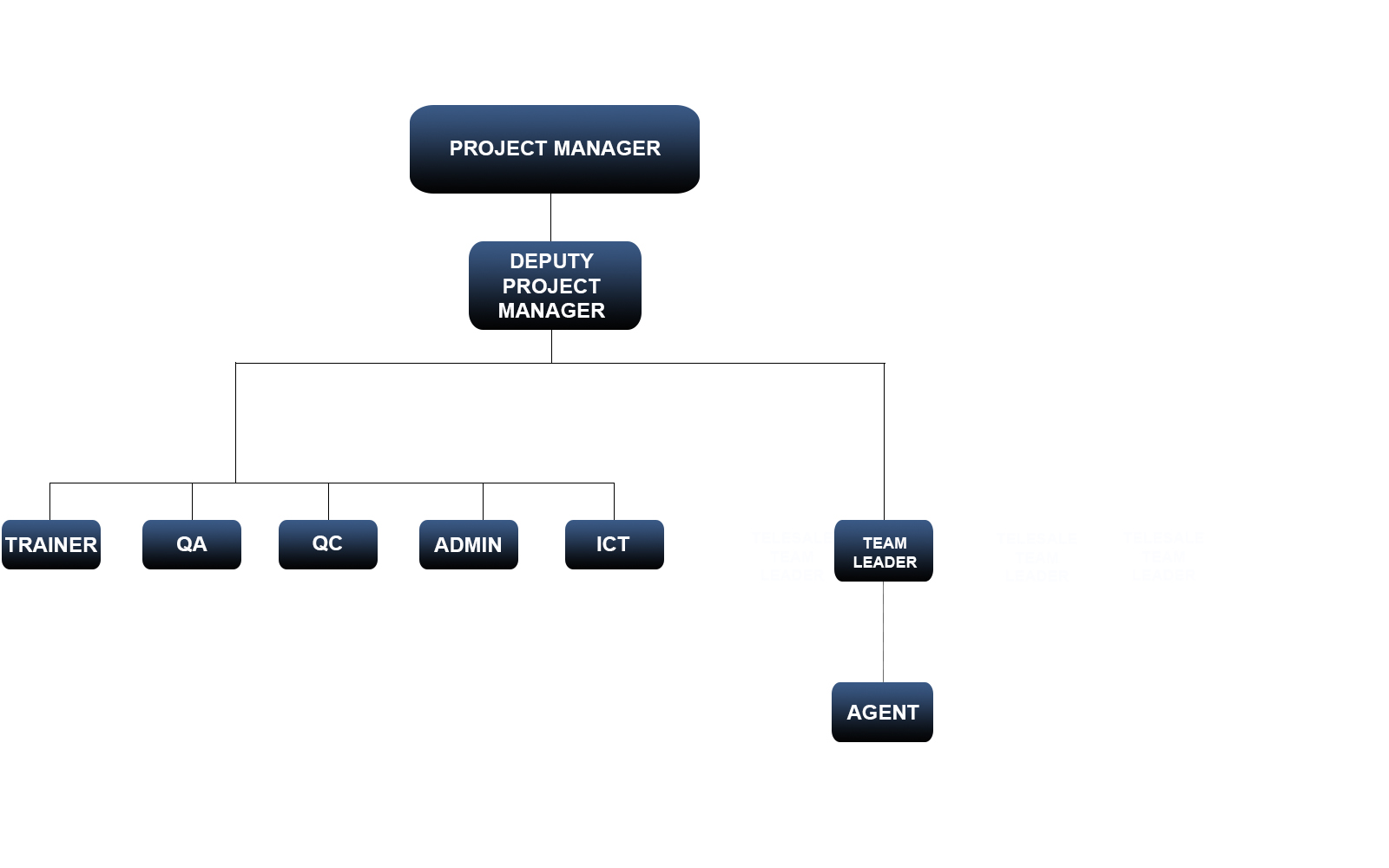
Note
- Project manager: Call center project manager
- Deputy project manager: Deputy project manager call center
- Team leader: Call center team leader, responsible for directly managing call center operators
- Agent: Operator
- Trainer: Call center training specialist
- QA (Quality Assurance): Quality Assurance
- QC (Quality Control) – Quality Control
- Admin: Manage administrative activities, documents,...
- ICT: Technical Support
Learn more: Customer service staff recruitment criteria
2. Prepare infrastructure, systems, equipment

Businesses need to set up facilities and infrastructure. Essential items for a stable Call Center operation include:
- Call center software
- Server system, network cable, power supply
- Office desks, computers, headphones.
- Proceed to install the information technology and telecommunications system. It is necessary to prepare and handle it well to ensure uninterrupted connection between, preferably Always have a backup device.
- Stable Internet connection (Recommended to have a backup Internet connection)
- Choose the switchboard number, should use the number 1900, 1800 if Inbound switchboard… Using the 1900 or 1800 number depends on the needs of the business.
Very few businesses invest in a professional Call Center system, because of the difficulties in implementation and the high investment costs. Instead, businesses often choose Call center outsourcing to save time, easy to manage and focus on core business development.
Important factors for good Call Center operation.
Affected by many factors, but there are 3 key factors after:
- Quality of recruitment department: Telephone operators are one of the personnel with a relatively high turnover rate. Having a high-quality recruitment department is a must for businesses to always be ready to back-up personnel and expand when necessary.
- Management and training effectiveness: The success or failure of a Call Center project depends largely on the Call Center Manager, who can inspire, provide training roadmaps, activities and connect employees. In addition, the quality of input training and regular retraining programs will help ensure the competence of call center agents.
- Internal communication effectiveness: Many businesses do not pay attention to this factor, especially for businesses with many different Call Center projects. The internal communications department will play the role of "making friends" to connect, motivate, build corporate culture and retain employees in the long term.
Criteria for evaluating call center
- Service Level Agreement (SLA): is the percentage of calls answered within a given time frame. According to statistics, the standard service level index in Call Center is 80% calls must be answered within 20 seconds.
- Average Reception Speed: is the average time it takes for calls to be attended to by an agent during a specific time period. This metric includes both the time customers spend waiting in a queue and the time the agent's phone rings, but does not include the time callers spend calling through the IVR system. According to global expert estimates, the Call Center Average Pickup Speed is 28 seconds.
- Missed Call Rate: The number of callers who hang up before an agent answers. The ideal global figure for this missed call rate is between 5 – 8%
- Call traffic forecast: is the number that represents the difference between the number of planned incoming calls predicted in a specific time frame and the number of actual incoming calls during that time period at the Call Center.
- Stick to the schedule Helps evaluate Call Center agents' compliance with assigned schedules.
- Completion rate: An index that evaluates the ability to complete work and the time it takes to complete calls of telephone operators (after the call).
- Call duration: is the time the operator spends talking to customers on the phone.
- Call end time: It is the amount of time a customer service representative needs after a call ends to complete all tasks related to the call.
- Rate of telephone operators on leave: is the number of days the operator is absent during the year as a percentage of the total number of working days in the contract.
- Attrition rate: is a measure of the annual turnover rate of customer service personnel of the enterprise, expressed as a percentage.
- Customer satisfaction: To get this parameter, businesses need to conduct customer surveys and then analyze the data to ensure accuracy.
- First call response rate: is the percentage of all calls where customer issues were resolved on the first call, with the agent not having to escalate the issue to a higher level for processing, call redirection, or call back.
See also:
Performance evaluation is very important, it not only determines the success of the call center but also has a significant impact on other business strategies.
15 Call Center Terms You Must Know
- Inbound: is a term that refers to calls/activities in which a business receives contact from customers.
- Outbound: term for activities in which businesses proactively call/contact customers.
- Telemarketing: Telemarketing (this is a loanword, created from “Telephone” + “Marketing”)
- Telesale: Telesales (Made from “Telephone” + “Sale”)
- BPO – Business Process Outsourcing: Outsourcing of a business's services/activities to serve business strategy, customer management, etc.
BPO Examples: Company A does not have enough potential to build its own customer care department (Call Center), and needs to hire an outside unit to do customer care work for their company for a certain period of time. BPO companies can provide both human resources, facilities, and technology as complete as a real department in a company.
6. Customer Relationship Management – Customer Relationship Management: Customer relationship management software.
7. Agent: Operator, telephone operator.
8. IVR – Interactive Voice Response: is a term that refers to automated voice interactions. For example, when a call comes in, the switchboard will automatically play a recording instructing the customer by pressing the number keys.
9. PBX – Private Branch Exchange: is an internal switchboard system, helping the company to be more convenient when employees exchange internally without incurring costs.
10. Voice over Internet Protocol – Voice over Internet Protocol: is a telephone switchboard that operates on the Internet platform based on IP connection.
11. ACD – Automatic Call Distribution: is a term referring to automatic call distribution systems. That is, when calls come to the switchboard, the system will automatically distribute them to the operators on duty in the queue.
12. Routing: Call routing. In the call center system, there are algorithms that route the call to which agent.
13. LCM – List & Campaign Management: Campaign management.
14. WFM – Workforce Management: Human resource management.
15. Omnichannel: Integrated multi-channel customer experience technology.







